4 Reporting
4.14 Supplementary and Other Information
4.14.5 Expenditures of Federal Awards (SEFA/Schedule 16)
4.14.5.10 The Uniform Administrative Requirements, Cost Principles, and Audit Requirements for Federal Awards 2 CFR 200 (Uniform Guidance), requires auditees to prepare a Schedule of Expenditures of Federal Awards (SEFA) for the period covered by the auditee’s financial statements. Click here for the Uniform Guidance.
If the government expends $750,000 or more in federal awards in a year, and audit is required by Uniform Guidance, 2 CFR 200, Subpart F – Audit Requirements. Governments must contact their local audit team to arrange for the audit and must submit the completed audit reporting package to the federal government within 30 calendar days after receiving the audit report (report issuance date) or within nine months following the end of the audit period, whichever is earlier. Governments that need a single audit must prepare financial statements even if they are not otherwise required to under the BARS Manual, the SEFA must be included as supplementary information. If the government received and spent federal funds under only one program, and the federal program’s statutes, regulations, or the terms and conditions of the federal award do not require a financial statement audit, the auditor may be able to conduct a program specific audit.
4.14.5.20 The purpose of this Schedule is to summarize federal award expenditures as a basis for planning and conducting the single audit. It also serves to provide assurance to those agencies that award federal financial assistance that their programs were included in the audit. It is important to prepare this Schedule carefully to ensure that it is accurate and complete. Any program or award expenditures omitted from this Schedule will be considered unaudited.
Determining Federal Awards Expended
4.14.5.30 Include on this Schedule all expenditures of federal awards that were received directly from a federal agency and indirectly (pass-through) from a state agency, local government or other nongovernmental entity.
4.14.5.40 Uniform Guidance: (2 CFR §200.510(b)) describes the requirements for preparing the Schedule. The SEFA must be prepared for the same period and reporting entity, and using the same underlying accounting records as the Schedule 01 and (as applicable) financial statements, except for specific exceptions described below starting at paragraph 4.14.5.70. The Schedule includes amounts required to be recorded, if any, during the statutorily required open period for cash basis cities and towns (20 days) and optional open period for cash basis counties (30 days to receive the invoice with the option to remain open for up to 60 days thereafter (per the county auditor’s discretion) to pay claims incurred prior to the close of the year).
Example: A calendar year government orders supplies and receives the supplies and invoice in December 2023. The government has an open period of 20 days after yearend. The government pays the invoice on February 5, 2024.
- Accrual basis: The expenditure is reported in the 2023 SEFA, because the activity, a receipt of goods in this situation, occurred during fiscal year 2023 and the invoice was received before the end of the period. In the financial statements this expenditure would have been reported as an expense with offsetting liability because it was not paid. Since the SEFA is reported on the same basis of accounting as the other financial reports, it too would report the expenditure.
- Cash basis: The expenditure is reported in the 2024 SEFA, because cash-basis entities report expenditures when paid. However, note that had this invoice been paid within the government's open period, a cash-basis city, town or county would report the expenditure on the 2023 SEFA (for more information on open period accounting, please see BARS 3.1.10 Accounting Principles).
Report award-related expenditures in the year they take place, even if the government will not be reimbursed by the awarding agency until the following year. For most programs, do not report amounts on this Schedule based on the date(s) that funds are received from the awarding agency (e.g., the date the government submitted a reimbursement request or received a reimbursement payment). See information on fixed amount awards below.
4.14.5.50 Federal awards expended include the following (2 CFR §200.1 Definitions Expenditures and §200.502 Basis for determining Federal awards expended):
- Direct costs of expenditure transactions associated with grants, cooperative agreements, direct appropriations, cost-reimbursement contracts under the Federal Acquisition Regulations (FAR), and other federal financial assistance.
- Indirect costs claimed for reimbursement using an indirect cost rate or cost allocation plan.
- Disbursement of federal award funds to subrecipients. (See additional information below regarding period of reporting.)
- Use of loan proceeds under loan and loan guarantee programs. (Refer to loan valuation guidance below.)
- Receipt of property (e.g., equipment and supplies), including some surplus property.
- Receipt or use of program income. (Refer to program income guidance below.)
- Receipt of non-cash assistance such as food commodities and vaccines.
- Disbursement of amounts entitling a non-federal entity to an interest subsidy.
- Insurance contracts in force during the period under audit.
4.14.5.60 Fixed Amount Awards
Fixed amount awards are a type of grant or cooperative agreement pursuant to which the Federal agency or pass-through entity provides a specific amount of funding without regard to actual costs incurred under the Federal award. For example, a fixed amount is paid for a specified deliverable met or milestone achieved. This type of Federal award reduces some of the administrative burden and record keeping requirements for both the recipient or subrecipient and the Federal agency or pass-through entity. Accountability is based primarily on performance and results. With fixed amount awards, the amount reported on the SEFA is the amount that was earned (amount to be paid per the terms and conditions) in the period it was earned, for example the deliverable was met or the milestone achieved.
Guidance for Specific Types of Costs
Equipment and supplies (non-cash assistance)
4.14.5.70 The receipt of federally-funded equipment, materials or supplies whether received directly from a federal agency or received indirectly from a pass-through agency is considered a non-cash award that must be reported on the SEFA. The recipient must report the fair market value at the time of receipt or the assessed value provided by the awarding agency of the non-cash items on the SEFA. Regardless of the basis of accounting used by the recipient, non-cash awards are reported in the fiscal year they are received.
Other non-cash assistance
4.14.5.80 Food stamps, food commodities, vaccines, donated property (including surplus), and other non-cash assistance should be valued at fair market value at the time of receipt or the assessed value provided by the awarding agency. The notes to the Schedule of expenditures of federal awards should disclose the nature of the amounts reported. Regardless of the basis of accounting used by the recipient, non-cash awards are reported in the fiscal year they are received.
Matching/cost sharing
4.14.5.90 The amount of state and/or local funding contributed by the entity in the form of matching funds or in- kind match required by the awarding agency should not be reported on the SEFA. If program regulations allow a federal award to be used as match, those expenditures would be reported on the SEFA.
Program income
4.14.5.100 Many awardees earn program income while administering federal programs or projects. For most programs, the receipt or use of program income is reported on the SEFA in the period the expenditure occurs in accordance with the basis of accounting. However, federal agencies differ on the treatment of program income on the SEFA. Therefore, it is recommended that the government consults with the awarding agency about how it requires the program income to be reported if not clear in the terms and conditions of the award or awarding agency guidance.
A note disclosure regarding the inclusion of expenditures from program income is recommended.
Note: For program specific requirements please see the Program Specific Packet.
Note: If the awardee has received written (documented) approval to use program income as match/cost sharing, it is not reported on the SEFA.
Note: See 4.14.5.140 section for accounting for program income related to revolving loans.
Unless otherwise specified in the awarding documents, interest earned on cash advances or idle award funds are not considered program income. Interest earnings are recorded in the BARS account 361.
Retainage
4.14.5.110 Retainage is an amount withheld from contractor payments until the end of the project when work has been completed to satisfaction. Per 2 CFR §200.305(b)(8), retainage is not an allowable cost that can be charged to the federal award and should not be reported on the SEFA as a federal expenditure until one of the following has been met
a) The retainage is paid to the contractor. Regardless of the basis of accounting used by the awardee, the retainage payment is reported in the fiscal year it is paid.
b) The retainage is paid into an escrow/trust account. Regardless of the basis of accounting used by the awardee, the retainage payment is reported in the fiscal year(s) it is paid into the escrow/trust account.
Note: If retainage was not paid to the contractor or paid to an escrow/trust account, but was incorrectly reimbursed by the awarding agency, a cash advance has occurred. Contact the awarding agency for instructions on what to do with the funds (such as return to them or move to an escrow/trust account).
Disbursements to subrecipients
4.14.5.120 Per 2 CFR §200.502, “the determination of when a Federal award is expended must be based on when the activity related to the Federal award occurs. Generally, the activity related to the Federal award pertains to events that require the non-Federal entity to comply with Federal statutes, regulations, and the terms and conditions of Federal awards, such as…the disbursement of funds to subrecipients…” Federal funds are determined to be expended when the pass-through agency becomes obligated to the subrecipient for payment. Generally that is when the pass-through agency has made the determination the costs are allowable, they are charged to the federal award, and the payment is made to (or authorized to be made to) the subrecipient.
Valuation of Federal Loans
4.14.5.130 Use the following guidelines to calculate the value of federal awards expended under loan programs:
- Amount of new loans made or received during the fiscal year, plus
- Beginning of the audit period balance of loans from previous years for which the federal government imposes continuing compliance requirements, plus
- Any interest subsidy, cash, or administrative cost allowance received.
Question 1: When do I report the loan on my SEFA?
Answer: Uniform Guidance: 2 CFR §200.502(a), and guidance from the AICPA states the loan is considered expended when the loan proceeds are used under loan and loan guarantee programs. Note exception to the rule for certain programs below.
- Reimbursement Basis: Most loans are funded on a reimbursement basis where the borrower incurs program-related costs and then makes a request to the lender for the loan proceeds. In this case, report expenditures during the year for which the government will seek loan funding.
- Loan Advances: Some loans are made in advance of any project-related expenditures. Because the federal government is at risk for these loans, the total proceeds received should be reported on the SEFA the date of receipt, even if the government has not spent all the funding. Contact the lender to determine if it requires the full amount of proceeds to be reported in the year of receipt.
- Revolving Loans: If the entity receives federal funds and then makes a loan to another party, report the amount of loans the government made during the year. (Refer to additional guidance on revolving loan funds below.)
Question 2: What is a continuing compliance requirement?
Answer: The government is considered to have a continuing compliance requirement if the lender continues to impose a requirement over the outstanding loan balance in any one of the following 12 areas in years following receipt of the loan.
- Activities allowed or unallowed
- Allowable costs/cost principles
- Cash management
- Eligibility
- Equipment and real property management
- Matching, level of effort, earmarking
- Period of performance of federal funds
- Procurement and suspension and debarment
- Program income
- Reporting
- Subrecipient monitoring
- Award-specific special tests and provisions, including federal wage rate requirements (David-Bacon Act)
Examples of continuing compliance requirements:
- A housing authority received a federal loan to construct apartments for low income households. As a condition of the loan, the authority is required to make a certain percentage of apartments available to low income households for the next 15 years. The housing authority should report the loan balance on the SEFA for the duration of this requirement. (We recommend consulting with the lender about its expectations for reporting loan balances.)
- A university has established a federal revolving loan fund and makes loans to students to help them pay for school expenses. The federal agency sponsoring the loan program requires the university to comply with continuing requirements such as default prevention, billing and collection, deferments, cancelations, fund liquidity, and borrower exit counseling.
- A city purchased equipment with loan funds and is required to maintain capital asset records and conduct physical inventories of the equipment in the years following the purchase.
Question 3: If my project takes several years to complete, will I have continuing requirements throughout the duration of the project until it is complete?
Answer: Most likely. For example, many lenders will set aside a portion of the funding until all inspections are made and all supporting documentation encompassing the entire project is submitted and approved. CAUTION: If the lender is waiting to reimburse a portion of costs submitted for reimbursement until the project is approved, be sure to report the expenditures in the year occurred, not when reimbursed. Consult with the lender about its expectations over reporting loans for projects that span multiple years.
Question 4: How do I determine the amount of any interest subsidy I am receiving?
Answer: The OMB has not issued any official guidance on this topic. Typically, an interest subsidy means the federal government is paying or waiving a portion of the interest cost that would ordinarily have to be paid by the borrower. Consult with the lender to determine if any portion of interest is being subsidized.
Question 5: What if my project is complete and there are no requirements other than to repay the loan?
Answer: If the laws, regulations, and the provisions of contracts or loan agreements pertaining to the loan impose no continuing compliance requirements other than to repay the loan, the loan does not have to be reported on the SEFA.
Question 6: What if our entity makes a loan to another entity or program participant?
Answer: Report the amount of loans made during the year. If the entity administers a revolving loan program where federal funds are lent to third parties, repaid, and then lent to again to other parties, the repayment of principal and interest is considered program income (revenues) and loans of such funds to eligible recipients are considered expenditures. For purposes of SEFA presentation, report the amount of loans the government made during the year. This includes all loans that are funded by the original loan and program income. However, be sure to check the terms of the award and discuss with the awarding agency because some federal agencies have different rules for presenting revolving loans on the SEFA. For example, the Department of Commerce for its Economic Adjustment Assistance Revolving Loan Fund program (ALN 11.307) requires awardees to report the principle balance of loans outstanding at year-end, instead of the amounts lent. See the Compliance Supplement Part 4 for this program, IV. Other Information for the specific calculation.
Reporting revolving loans
4.14.5.140 Although the repayment of principal is not considered revenue from the GAAP accounting perspective, it has to be considered as such for the purpose of SEFA. The expenditures from the revolving loan should include expenditures from the initial loan and subsequent repayments of the loans, including interest generated by the loan.
Employer Identification Number (EIN) for federal award recipients
4.14.5.150 Recipients of federal funds must arrange to have a single audit in accordance with Uniform Guidance, 2 CFR 200, Subpart F – Audit Requirements if they expend $750,000 or more in federal awards in a year. Most federal agencies define a recipient according to the federal Employer Identification Number (EIN). That is, the awarding agency makes its awards to each recipient based on the EIN, rather than entity name. For example, if a small fire district uses the county’s EIN for payroll tax purposes, and also applies for a federal award using the county EIN, some federal agencies will make the official award to the county. As a result, the awarding agency expects the award to be included in the county’s Schedule of Expenditures of Federal Awards (Schedule 16) and thus subject to audit at the county. Further, at the conclusion of a single audit, the fire district’s audit will be misfiled with the federal clearinghouse because the county’s EIN was listed on the Data Collection Form. This puts the county in a difficult position with the federal government and can cause additional audits. Therefore, it is recommended that all special purpose districts without an EIN make application for this number with the IRS (Form SS-4) and use this number when applying for federal financial assistance as well as IRS tax purposes. The district also should consult with its county auditor and/or treasurer for the protocol concerning payroll taxes.
Preparing the SEFA template for upload into the filing system
4.14.5.160 SEFA information may be manually input into the filing system or uploaded using the template from SAO’s website on the BARS Reporting Templates page. Instructions for the template are as follows:
Column A (ALN): Enter the Assistance Listing Number (ALN). If unknown or does not exist, follow detailed instructions below under number 3 included in Section 4.14.5.190.
Column B (COVID-19 Expenditures): Enter “Yes” if these are COVID-19 expenditures. As noted, COVID-19 expenditures must be reported separately by ALN. If these are not COVID-19 expenditures, please leave this column blank.
Column C (Federal Agency Name): The filing system will pre-populate the official federal agency name from SAM.gov Assistance Listings based on the ALN entered. However, if the ALN is unknown or doesn’t exist, manually add the federal agency name.
Column D (Federal Program Name): The filing system will pre-populate the official federal program name from SAM.gov Assistance Listings based on the ALN entered. However, if the ALN is unknown or doesn’t exist, manually add the federal program name.
Column E (Pass-through Agency Name): Enter the name of the pass-through agency for indirect awards. If there is no pass-through agency, leave this field blank.
Column F (Other Award I.D. Number): For indirect awards, add the other award identification number assigned by the pass-through agency (contract/agreement number). Refer to detailed instructions below. If no identification number was provided by the pass-through agency, enter “NA”. For direct awards, the other award identification number is optional and may be left blank.
Column G (R&D): Enter "Yes" if this award is research and development (R&D). Otherwise leave this column blank.
Column H (Total): Enter the total federal awards expended. Refer to detailed instructions below for calculating the total.
Column I (Passed Through to Subrecipients): Of the total amount of federal awards expended, report how much of that was passed on to subrecipients.
Column J (Footnote Reference): If applicable, enter the reference number that corresponds with the "Notes to the Schedule of Expenditures of Federal Awards."
Finalized Schedule of Expenditures of Federal Awards
4.14.5.170 Annual reports should be submitted via the filing system on the State Auditor’s website at: www.sao.wa.gov. Local governments have the option to import the SEFA data via the template or manually enter the data in the filing system. The example SEFA below is the formatted version that is generated by the filing system after the data is imported or manually entered.
4.14.5.180 Local governments are required to update the incorrect financial data submitted on this Schedule. The requirement applies to all errors found prior or during an audit. For questions and/or support e-mail the SAO Client HelpDesk through our Online Services.
Uniform Guidance Requirements for Reporting in the Clearinghouse
4.14.5.190 The following are detailed SEFA requirements found at 2 CFR §200.510(b). An example of a completed Schedule follows the instructions. Instructions for using the annual template are found above at 4.14.5.160.
1. List the name of the federal agency. If the government receives federal funds as a subrecipient, identify the pass-through agency.
2. List individual federal programs by federal agency. Provide the official name of the federal award from the Assistance Listings at SAM.gov (avoid nicknames, abbreviations, or acronyms).
As noted in the Program Specific Packet, COVID-19 expenditures must be reported on a separate line by ALN with “COVID-19” as a prefix to the program name, including new COVID-19 only programs, such as the Coronavirus State and Local Fiscal Recovery Fund 21.027.
IMPORTANT NOTE: For federal programs included in a cluster of programs, provide the official cluster name (e.g., CDBG – Entitlement Grants Cluster) regardless of whether the expenditures were incurred under only one program or multiple programs within the cluster, list the individual federal programs within the cluster (e.g., 14.218 Community Development Block Grants/Entitlement Grants and 14.225 Community Development Block Grants/Special Purpose Grants/Insular Areas) and provide a total for the cluster (see the example SEFA below). For research and development, total federal awards expended must be shown by either the individual award or by federal agency and major subdivision within the federal agency. A listing of programs included in a cluster can be found in Part 5 of the Compliance Supplement. Note the Compliance Supplement is updated annually, including the list of clusters found in Part 5, so it is important to consult the applicable Compliance Supplement (e.g., for audits of fiscal years beginning after June 30, 2023, consult the 2024 Compliance Supplement).
3. List the applicable ALN for each award. This is a five-digit (XX.XXX) identification number assigned by the federal government and published in Assistance Listings at SAM.gov. This number must be provided, for all federal awards received either directly from a federal agency or indirectly through a state agency or local government.
Awarding agencies are required to provide the ALN when making an award; however, if one was not provided, the government should make every effort to research the program before the government concludes an ALN does not exist. Steps to take:
- Contact the awarding agency.
- Search for the program on Assistance Listings at (SAM.gov).
- Check with other governments you know that also received the award
- Submit a question to the SAO Client HelpDesk.
If an Assistance Listing Number does not exist or is unknown, governments must use the following formula for the ALN:
Enter the Federal Agency’s two-digit prefix (see list of agencies in 4.14.5.190) followed by the letter “U”, for unknown, followed by a two-digit sequential number starting with “01”.
For example, if the government has two awards from the Department of Defense where the ALN does not exist or is unknown the government should report these awards using “12.U01” and “12.U02” as the ALN.
WARNING ERROR CAUTION: When entering an unknown ALN, you will get a “warning error”. That is because the filing system pulls from Assistance Listings at SAM.gov. If the ALN is unknown, it is not going to be in Assistance Listings. Also, if you enter an ALN that has been archived by the Federal Awarding Agency, in other words the program is no longer giving awards but you still have some federal expenditures to report, you will also get a warning error. In both of these cases, it is ok to ignore the warning error; you do not need to contact our Office.
4. For indirect awards or awards with an unknown ALN, list the identifying number assigned by the pass-through agency, such as the contract or agreement number. If an identification number is not available, or one was not provided in the awarding documents, enter "N/A". For direct awards with a known ALN, leave this field blank.
5. Report current year expenditures (determined on the same basis of accounting as the financial statements). See requirements for valuing loans and noncash assistance above.
Expenditures from Pass-Through Awards – Enter the amount of expenditures for federal assistance received as a pass-through award from a state agency, local government, etc. When calculating the amount expended for each program, be sure to include both direct costs and indirect costs. If the government made a subaward to another entity, these amounts should also be reported as expenditures.
Expenditures from Direct Awards – Enter the amount of expenditures for assistance received directly from a federal agency. When calculating the amount expended for each program, be sure to include both direct costs and indirect costs. If the government made a subaward to another entity, these amounts should also be reported as expenditures.
Note: If the entity receives an award under the same ALN from multiple awarding agencies, the SEFA should have a subtotal for that ALN showing the total amount received from all sources.
Total Expenditures – Enter the combined total of all federal expenditures from pass- through and direct awards by ALN.
6. List the total amount of expenditures provided to subrecipients for each federal award (2 CFR§200.510(b)(4)).
7. If applicable, enter the reference number that corresponds with the “Notes to the Schedule of Expenditures of Federal Awards.”
Instructions for preparing the Notes to the Schedule of Expenditures of Federal Awards
4.14.5.200 The order of Notes 1-3 corresponds to the Federal Audit Clearinghouse Data Collection Form (SF-SAC). Please follow the same order, as applicable. Order your remaining Notes sequentially.
REQUIRED NOTE 1 (per 2 CFR §200.510(b)(6)) – the notes to the Schedule must disclose the basis of accounting and any other significant accounting policies used in preparing the Schedule. This includes reconciling any difference between the amounts shown on the Schedule and the underlying amounts reflected in the entity’s accounting system.
REQUIRED NOTE 2 (per 2 CFR §200.510(b)(6)) – the notes must disclose whether or not the auditee elected to use the 10% de minimis cost rate as covered in 2 CFR §200.414 Indirect (F&A) costs. If the de minimis rate was not elected, it is optional to include the indirect cost rates used (see example below).
REQUIRED NOTE 3, IF APPLICABLE (per 2 CFR 200.510(b)(5)) – for loans or loan guarantee programs the notes must identify the balances outstanding at the end of the audit period. This is in addition to including the total federal awards expended for loan or loan guarantee programs reported in the Schedule.
OPTIONAL (BUT RECOMMENDED) – provide any information that may be useful to the reader such as the method used to value commodities or other non-cash assistance such as property or vaccines, and any other information necessary to reconcile the amount reported to the entity’s accounting records.
An example of these footnotes is provided below.
Frequently used federal agency two-digit prefixes
4.14.5.210 This list is used for ALNs; if the government does not see the federal agency here, Assistance Listings at SAM.gov.
07 – Office of National Drug Control Policy
10 – Department of Agriculture
11 – Department of Commerce
12 – Department of Defense
14 – Department of Housing and Urban Development
15 – Department of Interior
16 – Department of Justice
17 – Department of Labor
20 – Department of Transportation
21 – Department of Treasury
39 – General Services Administration
43 – National Aeronautics and Space Administration
47 – National Science Foundation
59 – Small Business Administration
64 – Department of Veterans Affairs
66 – Environmental Protection Agency
81 – Department of Energy (includes the Bonneville Power Administration)
84 – Department of Education
93 – Department of Health and Human Services
94 – Corporation for National Service
96 – Social Security Administration
97 – Department of Homeland Security (includes FEMA)
Characteristics of subrecipients and contractors
4.14.5.220 A subrecipient is a non-federal entity (typically a local government or non-profit organization) that receives federal assistance from a pass-through agency (such as the state or another local government) to carry out a program or project of the federal government. Subrecipients receive the federal award or loan so that it can meet a public need in the community. The amount paid to the subrecipient to reimburse it for the cost of the project or program should be based on actual, allowable costs incurred - that is, a subrecipient cannot earn a profit from its award. Subrecipients have substantial decision-making responsibility for how the project or program operates. Subrecipients are required to follow all applicable requirements in Uniform Administrative Requirements, Cost Principles, and Audit Requirements of Federal Awards, 2 CFR 200. Often subrecipients are required to contribute some of their own funds as a matching share to accomplish the program or project.
4.14.5.230 Contractors (formerly “vendors”) compete with others to provide goods and services needed to operate a project or program. These goods and services are often ancillary to the overall program objectives. Selection of contractors is typically based on the capability to provide the best goods and services at the best price. The scope of work is specified by the awardee and the price is usually based on quotes, formal bids, or requests for proposals. Contractors are often paid a set fee for providing its goods or services where the price allows the contractor to recover its costs and also earn a profit. The Association of Government Accountants (www.agacgfm.org) published a subrecipient versus contractor checklist.
Beneficiaries are not currently defined in the Uniform Guidance, however, a beneficiary is traditionally an individual who is the end user of the assistance (the individual needing the benefit). Examples include recipients of scholarships, Medicaid claims/medical benefits, or housing/food assistance. With certain Treasury COVID-19 programs, businesses, non-profits, and governmental entities may also be beneficiaries of assistance. Treasury’s Coronavirus State Local Fiscal Recovery Funds (SLFRF, ALN 21.027) Compliance and Reporting Guidance indicates that “subrecipients do not include individuals and organizations that received SLFRF funds as end users to respond to the negative economic impacts of COVID-19 on these organizations”. The organizations would be beneficiaries in this case. The Single Audit Act and 2 CRF Part 200, Subpart F regarding audit requirements do not apply to beneficiaries (no SEFA reporting).
4.14.5.240 Tips for preparing the Schedule
- Some projects or programs may be funded by a mix of federal and state money. If possible, identify the different sources and list them on appropriate Schedules (i.e., the federal share on the Schedule of Expenditures of Federal Awards and the state or portion on the Schedule of Expenditures of State Financial Assistance). If the state portion cannot be identified, list the entire amount on the Schedule of Expenditures of Federal Awards and describe the commingled nature of the funds in the notes to the Schedule of Expenditures of Federal Awards.
- Funds received as fee for services, generally should not be included on the Schedule 16. For example, if the government is being paid for providing goods or services in a contractor capacity, this contractor payment is not considered federal financial assistance to the entity.
- List all awards from the same federal agency together on the Schedule (for example, group all HUD awards together by ALN).
- If the government chooses to report multiple projects/programs that have the same ALN as separate line items (e.g., WSDOT highway planning and construction projects), provide a subtotal for the ALN.
- It is important to note that the expenditures reported on the SEFA will not necessarily tie to those reported on the operating statement, especially if the federal awards include loans or non-cash awards (property, supplies, etc.). However, all amounts reported should agree or reconcile to records maintained by finance, budget, and treasury departments.
- The SEFA should be prepared using the same basis of accounting as the financial statements. For example, if the government prepares the financial statements using the cash basis of accounting, the government should report expenditures of federal awards using the cash basis. Explain any departure in the footnotes.
4.14.5.250 Sample Schedule of Expenditures of Federal Awards
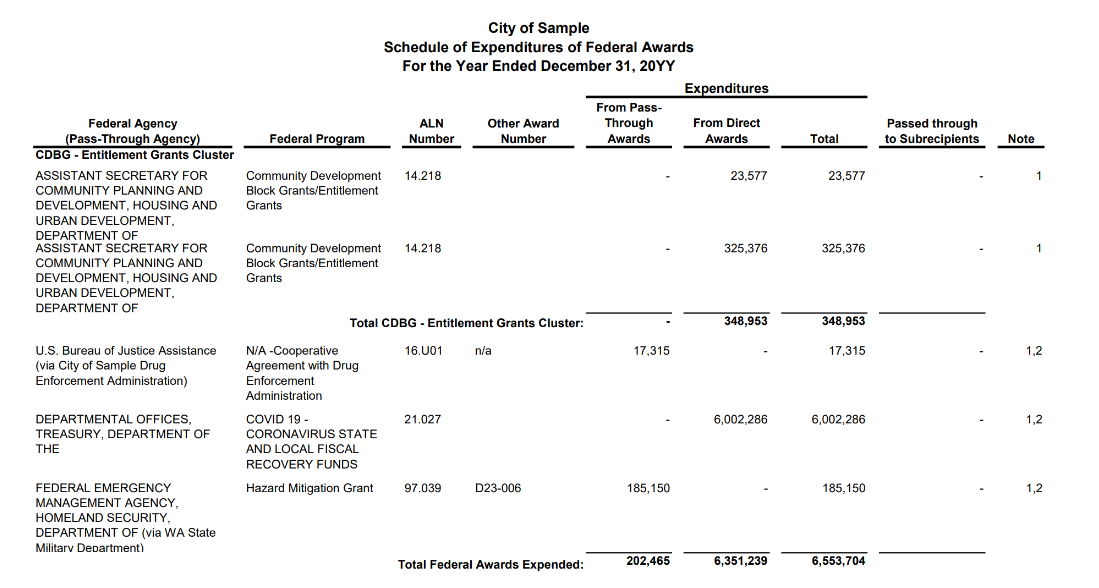
4.14.5.260 Template Notes to the Schedule of Expenditures of Federal Awards
________________________
(City/County/District)
Notes to the Schedule of Expenditures of Federal Awards
for the Year Ended December 31, 20XX
Please be advised the order of Notes 1-3 correspond to the Federal Audit Clearinghouse Data Collection Form (SF-SAC).
Please follow the same order, as applicable. Disclose other notes only if applicable to the government circumstances and in sequential order.
Note 1 – Basis of Accounting (Required)
This Schedule is prepared on the same basis of accounting (describe if not the same basis) as the (city/county/district’s) financial statements. The (city/county/district) uses the (describe the basis of accounting used by the city/county/district).
Note 2 – Federal Indirect Cost Rate (Required to state whether or not the de minis indirect cost rate was elected)
The (city/county/district) has not elected to use the 10-percent de minimis indirect cost rate allowed under the Uniform Guidance. The amount expended includes $______ claimed as an indirect cost recovery using an approved indirect cost rate of _____ percent.
or
The (city/county/district) has elected to use the 10-percent de minimis indirect cost rate allowed under the Uniform Guidance.
Note 3 – Federal Loans (Required if applicable)
(a) The (city/county/district) was approved by the USDA Rural Utilities Service to receive a loan totaling $____ to build a sewer treatment plant. Interim loan financing was received for the construction period. The amount listed for this loan includes the beginning of the period loan balance plus proceeds used during the year. The balance owing at the end of the period is $______.
(b) The (city/county/district) was approved by the EPA and the PWB to receive a loan totaling $____ to improve its drinking water system. The amount listed for this loan includes the beginning of the period loan balance plus proceeds used during the year. The balance owing at the end of the period is $_____.
Both the current and prior year loans are reported on the (city/county/district’s) (Schedule of Liabilities [Cash governments] or Schedule of Changes in Long-Term Liabilities [GAAP governments – note disclosure].
Note 4 – Revolving Loan – Program Income (Recommended if applicable)
The (city/county/district) has a revolving loan program for low income housing renovation. Under this federal program, repayments to the (city/county/district) are considered program revenues (income) and loans of such funds to eligible recipients are considered expenditures. The amount of loan funds disbursed to program participants for the year was $_____ and is presented in this Schedule. The amount of principal and interest received in loan repayments for the year was $____.
Note 5 – Noncash Awards (Recommended if applicable)
The amount of (vaccine/dental items/commodities/surplus property/etc.) reported on the Schedule is the value of (vaccine/dental items/commodities/surplus property/etc.) received by the (city/county/district) during current year and priced as prescribed by ________________.
Note 6 – Noncash Awards – Equipment (Recommended if applicable)
The (city/county/district) received equipment and supplies that were purchased with federal Homeland Security funds by the state of Washington. The amount reported on the Schedule is the value of the property on the date it was received by the (city/county/district) and priced by the state of Washington.
Note 7 – Program Costs (Recommended if applicable)
The amounts shown as current year expenditures represent only the federal award portion of the program costs. Entire program costs, including the (city/county/district’s) portion, are more than shown. Such expenditures are recognized following the cost principles contained in Title 2 U.S. Code of Federal Regulations Part 200, Uniform Administrative Requirements, Cost Principles, and Audit Requirements for Federal Awards, wherein certain types of expenditures are not allowable or are limited as to reimbursement.
